A new Apple patent (number ) at the US Patent & Trademark Office indicates that Apple has perhaps at least considered making a television set, as some folks are predicting. Of course, the patent for "positioning a first surface in a pre-determined position relative to a second surface," can also pertains to an iMac, a Cinema Display, even laptops.
The patent is for a method and an apparatus for positioning a first device in relation to a second device. An optical signal from a first device is sent to a second device. A reflection of the optical signal from the second device is received. A position of one of the devices relative to the other device is adjusted based upon the reflection. Gabriel G. Marcu is the inventor.
Here's Apple's background and summary of the invention: "Innovations in the computer display area have resulted in dramatic improvements of products that are used for displaying computer input and output. Monitors attached to computers have progressively become more space efficient along with being brighter and having higher resolution. Portable computers have become even more practical due to the advancements made in the field of computer displays.
"Innovations in this area have produced very thin displays that utilize small amounts of real estate while providing a quality display of computer graphics. For example, thin displays, such as those that are based upon liquid crystal display (LCD) technology, have been utilized.
One of the issues relating to thin displays, such as LCD screens, relates to the brightness and the quality of sections of the LCD screens. For example, much work has been dedicated to improving the brightness of LCD displays. Also, a large amount of effort has been dedicated to providing displays that provide more accurate colors and brightness when viewed at particular angles.
"One of the problems associated with the manufacture of LCD displays include manufacturing a number of LCD displays, such as LCD monitors, that have fairly consistent displays in terms of sharpness, contrast, color, and/or other features when viewed at various angles. When manufacturing LCD displays, a number of tests are performed on the various portions of the screen of the display for quality control.
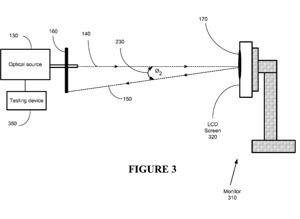
"Testing instruments are generally oriented at various angles, such as in a perpendicular orientation, and testing is then performed on the LCD screens as part of the manufacturing and testing processes. For example, testing includes measuring various colors on LCD screens according to predetermined standards, such as the ISO 13406 Standard. Often, a perpendicular orientation of the test instrument to the screen of the LCD monitor is used.
"The accuracy of the angle in relation to the test instrument and the LCD screen is important to the accuracy of the test performed on the display screen. One of the problems associated with the current methodology is that the test operator generally positions an instrument to the LCD screen utilizing approximations, which may cause delay and inaccurate test results. Additionally, a test angle used to analyze one LCD monitor may vary from the angle used to analyze another LCD monitor, thereby resulting in inconsistent test results of a batch of LCD monitors. Dedicating more time and resources to insure the accuracy of the angle between the test instrument and the LCD screen may cause inefficiencies (e.g., inaccurate testing, repeating screen adjustments, etc.) during the manufacturing and testing of computer displays, such as LCD monitors.
"The present invention is directed to overcoming, or at least reducing, one or more of the problems set forth above.
"In one aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for positioning a first apparatus in relation to a second apparatus. An optical signal from a first apparatus is sent to a second apparatus. A reflection of the optical signal from the second apparatus is received. A position of one of the apparatuses relative to the other apparatus is adjusted based upon the reflection.
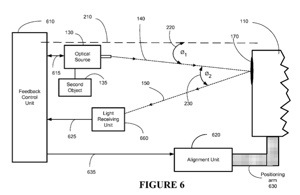
"In another aspect of the present invention, a system is provided for positioning a first apparatus in relation to a second apparatus. The system of the present invention includes an optical source affixed to the first apparatus. The optical source is provided for directing an incident light to the second apparatus. The system of the present invention also includes a light receiving unit to receive reflective light reflected from the second apparatus. The reflective light is used to adjust the positioning of the first apparatus in relation to the second apparatus.
"In another aspect of the present invention, an apparatus is provided for positioning a first device in relation to a second device. The apparatus of the present invention includes an optical source affixed upon the first device. The optical source includes a screen. The optical source is capable of providing an incident light that is directed towards the second device, from which a reflected light is received upon the screen. The apparatus is also capable of adjusting the relative positioning between the first and second devices based upon an angle of the reflected light.
"In yet another aspect of the present invention, a system is provided for positioning a testing unit in relation to a computer display. The system of the present invention includes a testing unit for performing a test upon the computer display or a television screen. The system of the present invention also includes an optical source affixed to the testing unit. The optical source is provided for directing an incident light to the computer display. The system of the present invention also includes a light receiving unit for receiving reflective light reflected from the computer display. The location of the light receiving unit upon which the reflective light is received is used to adjust the positioning of the testing unit in relation to the computer display."
-- Dennis Sellers